For industrial robots, handling materials is one of the more important applications in their handling operations. As a kind of working equipment with strong versatility, industrial robots can directly complete the task according to the clamping mechanism. Therefore, the clamping mechanism at the end of the robot should be designed according to the actual working tasks and the requirements of the working environment. This has led to a variety of structural forms of the clamping mechanism.
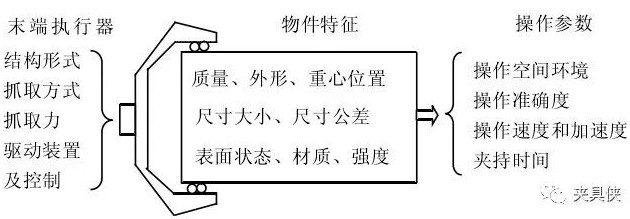
Figure 1 End-effector elements, features, parameters
Most mechanical clamping mechanisms are double-finger claw type. According to the finger movement mode, they can be divided into: rotary type and translation type; the different clamping methods can be divided into inner support type and outer clamp type; Pneumatic, electric, hydraulic and combination clamping mechanism.
1. Pneumatic end clamping mechanism
The gas source of pneumatic transmission is convenient to get, the action speed is fast, the working medium is non-polluting, and the fluidity is better than the hydraulic system, and the pressure loss is small, which is suitable for long-distance control. The following are several pneumatic manipulator devices:
1. Rotary type link lever type clamping mechanism
The fingers of the device (such as V-shaped fingers and curved fingers) are fixed to the clamping mechanism by bolts, and the replacement is convenient, so that the application of the clamping mechanism can be significantly expanded.
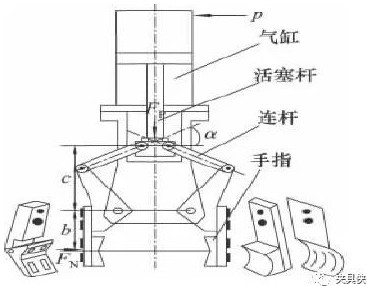
Figure 2 Back transformation linkage lever type clamping mechanism structure
2. Straight rod type double cylinder translation clamping mechanism
The finger end of the clamping mechanism is usually mounted on a straight rod equipped with a finger end mounting seat. When the pressurized gas enters the two rod chambers of the single-acting double cylinder, the piston is gradually moved to the middle until the workpiece is moved. Clamping.
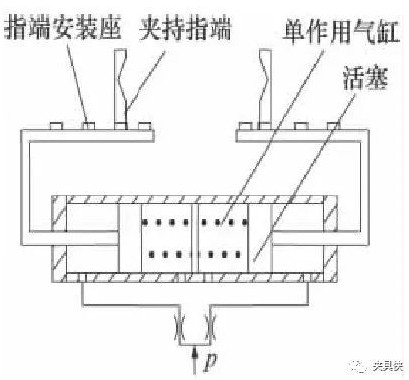
Figure 3 Structure diagram of the straight rod type double cylinder translation clamping mechanism
3. Connecting rod cross type double cylinder translation clamping mechanism
It is generally composed of a single-acting double cylinder and a crossed finger. After the gas enters the middle cavity of the cylinder, it will push the two pistons to move to the two sides, thereby driving the connecting rod to move, and the crossed fingertips will firmly fix the workpiece; if there is no air entering the intermediate cavity, the piston will act in the spring thrust With a lower reset, the fixed workpiece will be released.
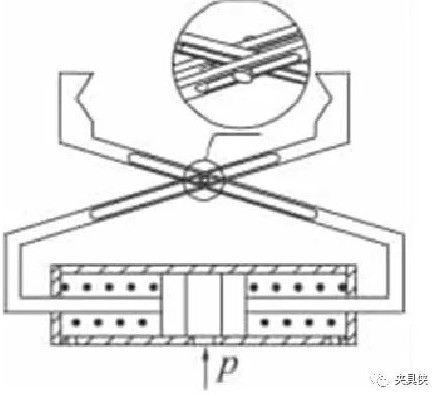
Figure 4 Cross-type two-cylinder translation clamping mechanism structure diagram
4. Internal support link lever type clamping mechanism
The force transmission is realized by a four-bar linkage mechanism, and the supporting direction is opposite to the outer clamping type, and is mainly used for grasping a thin-walled workpiece with an inner hole. After the clamping mechanism is fastened to the workpiece, in order to ensure that it can be positioned smoothly with the inner hole, usually three fingers are installed.
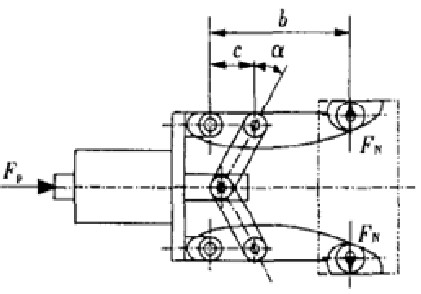
Figure 5 Structure diagram of the inner connecting rod lever type clamping mechanism
5. Fixed rodless piston cylinder driven force increasing mechanism
The pneumatic system of the fixed rodless piston cylinder is as follows. The cylinder is a single-acting cylinder, and the reverse direction is caused by the spring force. The two-way three-way solenoid valve realizes the commutation.
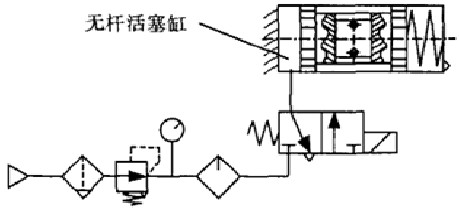
Figure 6 Pneumatic system of a fixed rodless piston cylinder
A transitional slider is mounted on the piston radial position of the rodless piston cylinder, and the two hinges are symmetrically hinged at both ends of the slider. If an external force acts on the piston, the piston will move left and right, thereby pushing the slider up and down. . When the system is clamped, the hinge point B will make a circular motion around point A, and the slider moves up and down to increase a degree of freedom, and the swing of the C point replaces the swing of the entire cylinder block.
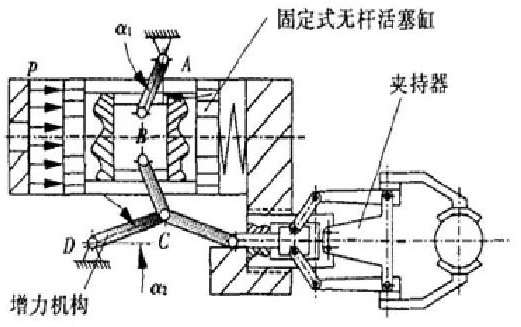
Figure 7 A booster mechanism driven by a fixed rodless piston cylinder
6. The internal clamping pneumatic device of the lever 2 series force increasing mechanism
When the directional control valve of the compressed air is in the left position working state shown in the figure, the left cavity of the pneumatic cylinder, that is, the rodless cavity, enters the compressed air, and the piston will move to the right under the action of the air pressure, so that the pressure angle α of the hinge is gradually reduced. Small, the air pressure is amplified by the angle effect, and then the force is transmitted to the lever of the constant force lever mechanism, and the force will be amplified again to become the force F for clamping the workpiece. When the directional control valve is in the right position, the right chamber of the pneumatic cylinder has a rod cavity to enter the compressed air, pushing the piston to the left, and the clamping mechanism releases the workpiece.
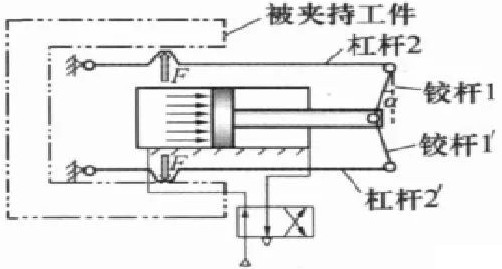
Figure 8 Internal clamping pneumatic manipulator of the lever 2 series tensioning mechanism
Second, the air suction type end clamping mechanism
The air suction type end clamping mechanism moves the object by the suction force formed by the negative pressure in the suction cup. It is mainly used to grab objects such as glass, paper, steel and other objects with large shape, moderate thickness and poor rigidity. According to the negative pressure generation method, it can be divided into the following types:
Squeeze suction cup
The air in the suction cup is squeezed out by the downward pressing force, causing a negative pressure inside the suction cup to form suction to attract the object. It is used to grasp workpieces with small shape, thin thickness and light weight.
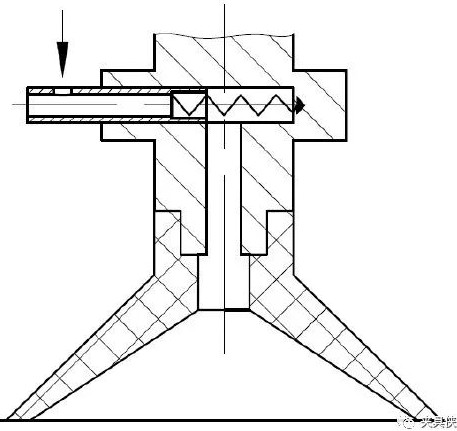
Figure 9 Squeeze suction cup structure
2. Airflow negative pressure suction cup
The control valve injects compressed air from the air pump from the nozzle, and the flow of the compressed air generates a high-speed jet, thereby taking away the air in the suction cup, so that a negative pressure is generated in the suction cup, and the suction formed by the negative pressure can be sucked. Workpiece.
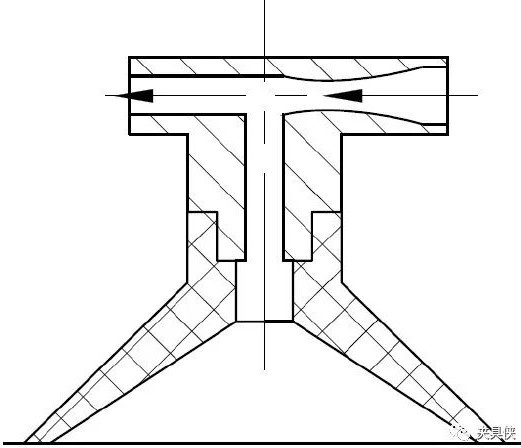
Figure 10 Airflow negative pressure suction cup structure
3. Vacuum pump exhaust suction cup
The electromagnetic pump is used to connect the vacuum pump to the suction cup. When the air is sucked away in the suction chamber, a negative pressure is formed to attract the object. Conversely, when the control valve connects the suction cup to the atmosphere, the suction cup loses suction and releases the workpiece.
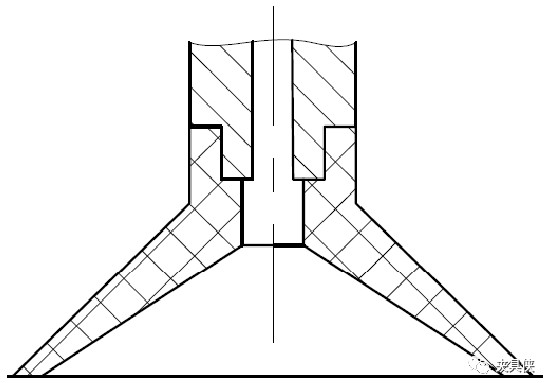
Figure 11 Vacuum pump venting suction cup structure
Third, the hydraulic end clamping mechanism
1. Normally closed clamping mechanism
The drill is fixed by the strong preload of the spring and the hydraulic pressure is released. When the clamping mechanism does not perform the grasping task, it is in the state of clamping the drill. The basic structure is a set of pre-compressed springs acting on a force-increasing mechanism such as a slope or a lever, so that the slip seat generates axial movement, which drives the slip to move radially, and clamps the drill; the high-pressure oil enters the slip seat and The hydraulic cylinder formed by the outer casing further compresses the spring, causing the slip seat and the slip to reverse movement and loosen the drill.
2. Normally open clamping mechanism
The spring is loosened and hydraulically clamped, and is released when the grabbing task is not performed. The clamping mechanism generates a clamping force by the thrust of the hydraulic cylinder. The reduction of the oil pressure will result in a reduction of the clamping force. Usually, a hydraulic lock with a reliable performance is provided on the oil circuit to maintain the oil pressure.
3. Hydraulic elastic clamping mechanism
The loosening and clamping are all realized by hydraulic pressure. If the oil inlets of the hydraulic cylinders on both sides are connected to the high-pressure oil, the slip will gather toward the center with the movement of the piston, clamp the drilling tool, change the high-pressure oil inlet, and the slip will deviate from the center. , loosen the drill.
4. Composite hydraulic clamping mechanism
The device has a main hydraulic cylinder and a secondary hydraulic cylinder, and a pair of disc springs are connected to the auxiliary hydraulic cylinder side. When the high pressure oil enters the main hydraulic cylinder, the main hydraulic cylinder is driven to move, and the force is transmitted to the auxiliary hydraulic cylinder side through the top column. In the slip seat, the disc spring is further compressed, and the slip seat moves; at the same time, the main cylinder side slip seat moves under the action of the spring force to release the drill.
Fourth, the magnetic end clamping mechanism
Divided into electromagnetic suction cups and permanent suction cups. The electromagnetic chuck sucks and releases ferromagnetic objects by turning on and off the current in the coil, generating and eliminating magnetic forces. The permanent magnet sucker uses the magnetic force of the permanent magnet to attract the ferromagnetic object. It moves the magnetic separation object to change the magnetic line circuit in the suction cup, thereby achieving the purpose of sucking and releasing the object. But the same is the suction cup, the suction of the permanent suction cup is not as large as the electromagnetic suction cup.
Volleyball Court PVC Sports Flooring
Volleyball Court Pvc Sports Flooring,Mat Flooring For Volleyball,Pvc Volleyball Mat Flooring,Indoor Volleyball Court Flooring
Jiangsu Ruidong Sports Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.cnruidongsports.com